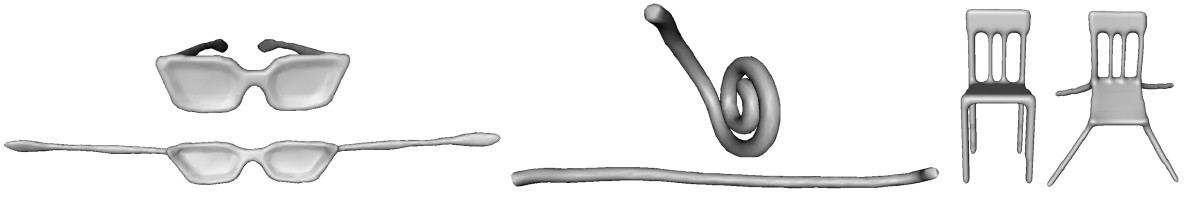
AbstractWe present a shape deformation algorithm that unfolds any given 3D shape
into a canonical pose that is invariant to non-rigid transformations. Unlike
classical approaches, such as least-squares multidimensional scaling, we
preserve the geometric details of the input shape in the resulting shape,
which in turn leads to a content-based non-rigid shape retrieval application
with higher accuracy. Our optimization framework, fed with a triangular or
a tetrahedral mesh in 3D, tries to move each vertex as far away from each
other as possible subject to finite element regularization constraints. Intu-
itively this effort minimizes the bending over the shape while preserving the
details. Avoiding geodesic distances in our computation renders the method
robust to topological noise. Compared to state-of-the-art approaches, our
method is simpler to implement, faster, more accurate in shape retrieval,
and less sensitive to topological errors.
PublicationYusuf Sahillioglu, Ladislav Kavan. Detail-preserving Mesh Unfolding for Non-rigid Shape Retrieval. ACM Transactions on Graphics 35(2) [Presented at SIGGRAPH], 2016.  
Links and DownloadsPaper
 | | BibTeX
 | | Supplemental document
 | | Code (Visual Studio)
 |
AcknowledgementsWe thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive com-
ments, and Norm Badler, James O'Brien, Tiantian Liu, Mark Pauly
and Lifeng Zhu for fruitful discussions. This work was supported
by TUBITAK under the project EEEAG-115E471, and the NSF
awards IIS-1622360 and IIS-1350330.  |